HEPA filters are essential components in modern air filtration systems such as air purifiers, cleanrooms in healthcare, microbiological laboratories, and industrial HVAC systems. So, what exactly is a HEPA filter, how does it work, and what is it made of? Let’s explore in detail below.
HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air) filters are high-performance air filters capable of trapping at least 99.97% of airborne particles as small as 0.3 microns – considered the most penetrating particle size (MPPS) in aerodynamic filtration.
Residential and industrial air purifiers
Cleanrooms in healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and electronics
Biosafety cabinets
Central HVAC systems
HEPA filters purify air through a combination of three primary mechanisms:
Interception: Captures particles when they come close to filter fibers.
Impaction: Larger particles deviate from airflow paths and collide with the fibers.
Diffusion: Ultrafine particles are deflected by gas molecules and get trapped easily.
Thanks to these three mechanisms, HEPA filters effectively remove PM2.5 fine dust, bacteria, mold, and viruses.
Note: Modern HEPA filters may also incorporate electrostatic attraction to enhance filtration performance.
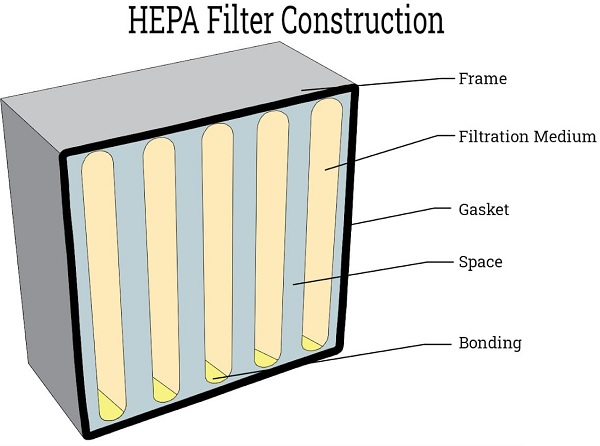
A standard HEPA filter typically consists of three main components:
Filter media: Made from ultra-fine glass fibers or synthetic polymer fibers arranged randomly for maximum surface area.
Frame: Constructed from aluminum, stainless steel, or ABS plastic, providing structural stability.
Sealant or gasket: Prevents air leaks between the filter and housing unit.

| Type | Filtration Efficiency | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| H10 – H12 | 85% – 99.5% | Home air purifiers |
| H13 | ≥ 99.95% | Low-grade cleanrooms, medical devices |
| H14 | ≥ 99.995% | High-grade cleanrooms, biosafety cabinets |
| ULPA (U15–U17) | ≥ 99.9995% | Ultra-clean environments (e.g., semiconductors, microbiology) |
Exceptionally high filtration efficiency, meeting cleanroom and medical standards
Effectively filters out fine dust, bacteria, and viruses
Safe and eco-friendly – no harmful emissions
Long lifespan: 6 to 12 months depending on environment
Easy integration into air filtration systems or HVAC setups
The filter media material determines the efficiency and durability of the HEPA filter. Currently, there are three main types:
Used since the 1950s, this material offers:
Stable performance throughout lifespan
Excellent dust-holding capacity
Long lifespan, reducing replacement cost
Note: Glass fiber is fragile and sensitive to impact. It should be handled and installed by trained technicians.
Developed in the late 1990s, this material:
Reduces initial resistance, saving energy
However, performance may degrade due to dust or humidity
Recommendation: Suitable for energy-saving systems, but not ideal for cleanrooms or high-reliability environments.
The most advanced filtration material today, offering:
Low energy consumption
High mechanical strength and long life
Stable efficiency under harsh conditions – ideal for healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and electronics manufacturing
Summary: Multi-fiber polymer is becoming the top choice for modern HEPA filtration systems.
Choosing the right HEPA filter material maximizes filtration efficiency, extends equipment lifespan, and reduces maintenance costs. Depending on your application, consider:
Glass fiber: Reliable for demanding environments
Membrane media: Energy-efficient, but performance-sensitive
Multi-fiber polymer: Comprehensive solution and emerging trend for cleanrooms and high-end systems
1. Can HEPA filters remove viruses?
Yes. Due to the diffusion mechanism, HEPA filters can trap ultrafine particles like viruses, even those smaller than 0.3 µm.
2. How often should HEPA filters be replaced?
Homes and offices: Every 6–12 months
Cleanrooms and medical environments: Every 3–6 months (based on manufacturer guidelines)
3. Are HEPA filters reusable?
No. HEPA filters are single-use and should not be washed, as doing so will compromise their performance.
4. How do HEPA filters differ from regular filters?
Regular filters only capture large particles and are ineffective against fine dust or microbes. In contrast, HEPA filters offer ultra-clean filtration suitable for medical, research, and precision industries.
BACH LONG TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD
Address: 75 Nguyen Hong Street, Ward 1, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City
Hotline: 093 143 54 54
Email: sales@congnghelockhi.vn
Website: www.congnghelockhi.vn